Indoor Air Quality Tips to Fight Diseases
In today’s fast-paced world, people spend the majority of their time indoors, making the quality of indoor air more crucial than ever. Poor indoor air quality can lead to various serious health problems and issues, including respiratory problems, allergies, and even severe diseases. In this article, we will explore essential tips for improving indoor air quality to combat diseases and enhance your overall well-being. By implementing these tips, you can create a healthier and more comfortable living environment for yourself and your loved ones.
1. Regular Ventilation
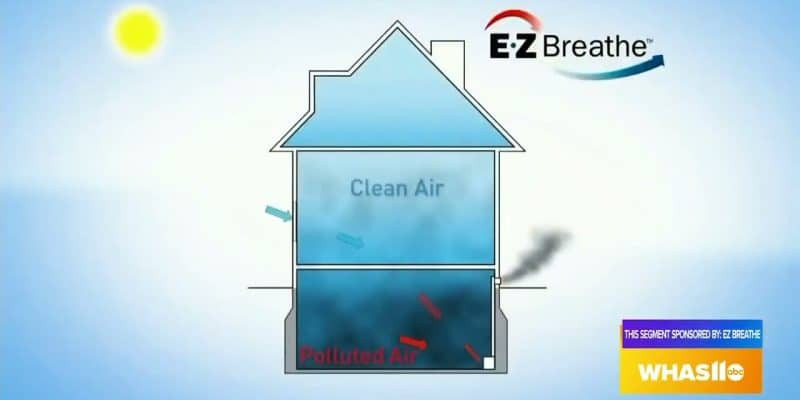
Regular ventilation is a cornerstone of ensuring healthy indoor air quality. It plays a crucial role in promoting the circulation of fresh outdoor air while expelling indoor air pollutants. Here, we will delve deeper into the importance of regular ventilation and provide practical tips for incorporating it into parts of your daily routine.
The Significance of Regular Ventilation:
- Removal of Indoor Pollutants: Homes can accumulate a variety of pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from cleaning products, pet dander, mold spores, and dust mites. These pollutants can exacerbate allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions. Regular ventilation helps remove these contaminants from your indoor environment, leading to cleaner, healthier air.
- Disease Prevention: Proper ventilation can mitigate the risk of airborne diseases, such as influenza and COVID-19. Adequate ventilation dilutes and disperses potentially infectious aerosols, reducing the likelihood of transmission. During the ongoing pandemic, ensuring good ventilation in indoor spaces has been recognized as a crucial safety measure.
- Comfort and Well-being: Good indoor air quality promotes comfort and well-being. Stale, stuffy air can make occupants feel lethargic and unwell. Fresh air, on the other hand, can enhance concentration, mood, and overall quality of life.
Practical Tips for Regular Ventilation:
- Open Windows and Doors: One of the simplest ways to ventilate your home is to open windows and doors. Aim to do this for at least a few minutes each day. Even during inclement weather or cold seasons, a brief daily airing can significantly improve indoor air quality.
- Use Exhaust Fans: In areas where moisture and odors are common, such as the kitchen and bathroom, make use of exhaust fans. These fans draw out stale air and bring in fresh air from outside. Regular use of exhaust fans can also help prevent mold growth in these areas.
- Cross-Ventilation: Create cross-ventilation by opening windows on opposite sides of your home. This allows for a gentle breeze to flow through, carrying pollutants away and replenishing the indoor air with outdoor air. Cross-ventilation is especially effective during milder weather.
- Scheduled Ventilation: Establish a schedule for ventilation, such as opening windows during your morning routine or before bedtime. Consistency in your approach to ventilation ensures that you regularly refresh the air in your home.
- Night Ventilation: Nighttime can be an ideal opportunity for ventilation. The air is often cooler and cleaner, and the reduced noise from outdoor activities can make nighttime ventilation more pleasant.
- Invest in Mechanical Ventilation: For homes with insufficient natural ventilation, consider investing in mechanical ventilation systems. These systems exchange indoor air with fresh outdoor air continuously. They come in various types, such as heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), which also help maintain indoor temperatures.
In summary, regular ventilation is a powerful tool for improving indoor air quality and safeguarding against diseases. By incorporating these practical tips into your daily routine, you can ensure that your home is a haven of fresh, clean air, which is essential for your health and overall well-being. Prioritizing less air pollution through regular ventilation is a proactive step toward a healthier and more comfortable living space.
2. Use Air Purifiers
Using air purifiers is a highly effective and increasingly popular method for enhancing indoor and outdoor air quality. These devices are designed to remove a wide range of airborne pollutants, from dust and allergens to microorganisms and even odors. Let’s explore the importance of using air purifiers and provide more information about how they work and what to consider when selecting one.
The Importance of Using Air Purifiers:
- Allergen Reduction: Air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters are excellent at capturing and removing allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with allergies or asthma, as cleaner air can significantly reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Pathogen Removal: Air purifiers can trap and neutralize microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses. This is particularly relevant during flu seasons and in situations where infection control is essential. The use of air purifiers can help reduce the risk of respiratory illnesses and protect the health of occupants.
- Odor Elimination: Air purifiers with activated carbon filters can effectively remove odors from cooking, pets, smoke, and other sources. This is especially valuable in homes where unwanted odors can be persistent and unpleasant.
- Improved Respiratory Health: Cleaner air reduces the exposure to irritants that can trigger or exacerbate respiratory conditions. Using an air purifier can help alleviate symptoms for those with asthma, bronchitis, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
How Air Purifiers Work:
Air purifiers operate by drawing in air from the room and passing it through a series of filters designed to capture specific particles and pollutants. The key components of indoor air pollution will include:
- Pre-Filter: A pre-filter captures larger particles like dust and pet hair, preventing them from clogging the main filter and increasing its lifespan.
- HEPA Filter: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are highly effective at trapping particles as small as 0.3 microns, including pollen, mold spores, and pet dander. These filters are a standard feature in most quality air purifiers.
- Activated Carbon Filter: Activated carbon filters are designed to adsorb odors, gases, and chemicals. They are particularly useful for removing cooking odors, pet odors, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- UV-C Lights or Ionizers: Some air purifiers include additional features like ultraviolet (UV-C) lights or ionizers, which can kill or neutralize bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. These features provide an extra layer of protection against pathogens.
What to Consider When Selecting an Air Purifier:
When choosing an air purifier, consider the following factors:
- Room Size: Ensure the air purifier is appropriately sized for the room where you intend to use it. Manufacturers typically specify the maximum room size a unit can effectively clean.
- Filter Type: Choose an air purifier with the appropriate filter for your needs. For allergen removal, HEPA filters are a must. For odor control, look for activated carbon filters.
- Noise Level: Some air purifiers can be noisy, which may be distracting or disruptive in quiet environments. Look for quieter models if this is a concern.
- Maintenance: Regular filter replacement is essential to maintain the effectiveness of your air purifier. Consider the cost and availability of replacement filters when making your purchase.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for Energy Star-rated air purifiers, which are designed to be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Using air purifiers is a practical and proactive step toward improving indoor air quality and protecting your health. Whether you’re concerned about poor air quality, allergies, respiratory conditions, or the overall comfort of your living space, a well-chosen air purifier can make a significant difference in creating a cleaner and healthier home environment.
3. Control Humidity Levels
Controlling humidity levels within your home is an essential aspect of maintaining optimal indoor air quality. Humidity, the amount of moisture in the air, can have serious health effects and a significant impact on both your health and the comfort of your living environment. Here’s a more detailed look at the importance of controlling humidity levels and some practical tips for doing so:
The Importance of Controlling Humidity Levels:
- Mold and Mildew Prevention: High humidity levels can promote the growth of mold and mildew, which release allergenic spores into the air. Exposure to mold can trigger allergies and asthma symptoms and lead to various health issues.
- Respiratory Health: Maintaining an appropriate humidity level helps prevent dry indoor air, which can irritate the respiratory system. Dry air can lead to conditions like dry skin, and irritated eyes, and exacerbate existing respiratory problems.
- Thermal Comfort: Controlling humidity levels can impact how comfortable your home feels. Air that is too humid can make your space feel hot and stuffy, while overly dry air can lead to discomfort and the need for additional heating in the winter.
- Energy Efficiency: By maintaining the right humidity levels, you can help regulate indoor temperatures more effectively, which can reduce the need for energy-consuming heating or cooling.
Practical Tips for Controlling Humidity Levels:
- Use a Hygrometer: A Hygrometer is a device that measures humidity levels in your home. By regularly monitoring your indoor humidity, you can adjust your efforts accordingly.
- Use a Dehumidifier: If you live in a humid climate or have humidity levels consistently above 50%, consider using a dehumidifier. Dehumidifiers remove excess moisture from the air, preventing mold growth and improving comfort.
- Use a Humidifier: In dry climates or during the winter months, a humidifier can add moisture to the air, preventing dry skin, irritated nasal passages, and respiratory discomfort. It can also help reduce static electricity in the home.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation, as mentioned in the previous sections, can also help control humidity levels. Ventilate your home during times of high humidity to remove excess moisture, and use exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms to reduce indoor humidity.
- Seal Leaks: Inspect your home for air leaks and moisture entry points, such as around windows and doors. Proper sealing can prevent outdoor moisture from entering your home.
- Keep Indoor Plants in Check: Indoor plants release moisture into the air as part of their natural respiration process. While this can be beneficial, too many plants can contribute to high humidity levels. Adjust the number of plants to maintain a comfortable humidity level.
- Use A/C and Heating Systems: Modern air conditioning and heating systems often include humidity control features. Use these systems to regulate indoor humidity as needed, especially if they include a dehumidification option.
- Air Circulation: Promote air circulation within your home with the help of fans. This can help distribute moisture evenly and create a more comfortable environment.
By controlling humidity levels in your home, you can significantly enhance indoor air quality and your overall living experience. Maintaining a balanced humidity level not only safeguards against mold and mildew but also improves respiratory health and comfort. Be mindful of your specific climate and the changing seasons, as adjustments may be necessary to maintain the ideal indoor humidity level, found in homes, typically around 30-50%.
4. Maintain HVAC Systems
Maintaining your Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems is a critical aspect of ensuring good indoor air quality. These systems play a central role in acceptable indoor air quality by regulating temperature, humidity, and air circulation within your home. Neglecting HVAC maintenance can lead to a variety of indoor air quality problems and impact your health. Here’s a closer look at the importance of maintaining HVAC systems and some tips to keep them in top condition:
The Importance of Maintaining HVAC Systems:
- Improved Air Quality: HVAC systems can become breeding grounds for dust, mold, and other contaminants if not properly maintained. A neglected system can circulate these pollutants throughout your home, leading to respiratory issues and allergies.
- Energy Efficiency: A well-maintained HVAC system operates more efficiently. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and parts replacement when needed, can result in lower energy consumption and utility bills.
- Longevity: Consistent maintenance can extend the life of your HVAC system. Replacing an entire system is a significant investment, so prolonging its lifespan through maintenance is a cost-effective strategy.
- Comfort: Regular maintenance ensures that your HVAC system can effectively regulate temperature and humidity, leading to a more comfortable living environment.
Practical Tips for Maintaining HVAC Systems:
- Change Filters Regularly: One of the simplest yet most effective maintenance tasks is changing the air filters. Dirty filters can impede airflow and allow contaminants to recirculate. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for filter replacement, which is typically every 1 to 3 months.
- Inspect and Clean Ductwork: Over time, dust, debris, and even mold can accumulate in the ducts. Periodic inspection and cleaning of the ductwork can prevent these contaminants from entering your living spaces. Consider professional duct cleaning if you suspect a significant buildup.
- Schedule Professional Maintenance: Hire a qualified HVAC technician to perform routine inspections and maintenance. Professionals can identify and address issues you might miss, ensuring that your system operates optimally. A typical maintenance visit includes cleaning, lubricating moving parts, and checking for leaks and refrigerant levels.
- Check for Leaks: Ensure that your HVAC system is not leaking refrigerant or water. Leaks can damage the system and negatively impact air quality. Address leaks promptly to prevent further damage and potential mold growth.
- Keep Outdoor Units Clean: If you have an outdoor HVAC unit (e.g., a condenser unit), keep it clean and free of debris. Ensure there is adequate clearance around the unit for proper air circulation. Clean the coils and the area around the unit periodically.
- Balance Humidity Levels: If your HVAC system includes humidity control features, use them to maintain optimal indoor humidity. Proper humidity levels help prevent mold growth and improve comfort.
- Programmable Thermostats: Install and use programmable thermostats to regulate temperature when you are away from home. This reduces unnecessary HVAC system operation, saving energy and reducing wear and tear.
- Consider Regular Inspections: Even outside of scheduled maintenance, consider having your HVAC system inspected annually. An inspection can catch issues early, preventing them from becoming major and costly problems.
In conclusion, the quality of indoor air is a vital component of a healthy and comfortable living environment. Poor indoor air quality can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, allergies, and even diseases. To combat these concerns and enhance your well-being, it’s crucial to implement a set of effective air exchange strategies.
Regular ventilation helps to circulate fresh outdoor air, reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants. Using air purifiers can significantly reduce airborne air contaminants, making the air cleaner and safer to breathe. Controlling humidity levels prevents mold growth and contributes to a more comfortable indoor atmosphere. Finally, maintaining HVAC systems ensures optimal air quality and energy efficiency.
By adopting these practices, you can create a safer and more comfortable living space that supports your health and well-being. Remember that a proactive approach to indoor air quality is an investment in a healthier and more enjoyable life. Prioritizing indoor air quality is not just a choice; it’s a commitment to a better, disease-free future for the environmental health of you and your loved ones.