The Power of Fresh Air Exploring the Importance of Indoor Ventilation
In our modern lives, where we spend a significant amount of time indoors, whether at home, in the office, or in other enclosed spaces, it is crucial to understand the importance of indoor ventilation. While we often focus on creating comfortable and aesthetically pleasing environments, we must not overlook the crucial role that indoor ventilation plays in maintaining a healthy and pleasant indoor atmosphere. Adequate indoor ventilation is essential for promoting good air quality, regulating temperature and humidity levels, and ensuring the overall well-being of occupants.
What is Indoor Ventilation?
Indoor ventilation is a fundamental aspect of maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. It involves the exchange of air between the indoors and outdoors, ensuring a constant supply of fresh air while removing stale air and pollutants from enclosed spaces. Ventilation can occur naturally through openings such as windows, doors, and vents, or it can be facilitated by mechanical systems specifically designed for air exchange.
Natural ventilation takes advantage of air pressure differences and wind flow to drive the movement of air. When windows or doors are opened, fresh air enters the space while stale air is expelled. This process allows for the circulation of air and the removal of pollutants, moisture, and odors. Natural ventilation is particularly effective in moderate climates and during seasons with pleasant weather conditions.
Mechanical ventilation, on the other hand, relies on mechanical systems to ensure consistent and controlled airflow. These systems can be categorized into various types, including exhaust fans, supply fans, and balanced ventilation systems. Exhaust fans are commonly used in areas such as kitchens and bathrooms, where removing odors, moisture, and contaminants is essential. Supply fans, on the other hand, introduce fresh outdoor air into a building, replacing stale indoor air. Balanced ventilation systems combine both exhaust and supply mechanisms, providing a balanced airflow throughout the building.
In addition to natural and mechanical ventilation, there are specialized ventilation systems designed for specific purposes. For example, energy recovery ventilation (ERV) systems recover heat or coolness from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming air, thus improving energy efficiency. Heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems specifically focus on heat exchange, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature while ensuring a fresh air supply.
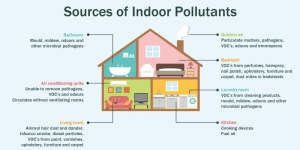
The process of indoor ventilation serves several purposes beyond just air exchange. It helps regulate temperature and humidity levels, remove pollutants, control odors, and prevent the buildup of excess moisture. By promoting good indoor air quality, ventilation contributes to the overall health and well-being of occupants. Proper ventilation prevents the accumulation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), allergens, dust particles, and other pollutants that can have adverse effects on respiratory health and overall comfort.
Moreover, ventilation plays a significant role in air pollution and preventing the growth of mold, mildew, and other harmful microorganisms. By controlling moisture levels and allowing for the drying of damp areas, ventilation helps maintain the structural integrity of buildings and prevents the development of indoor air quality issues.
It is important to note that different buildings and spaces require different ventilation strategies based on factors such as size, occupancy, and intended use. Proper ventilation design considers factors like air exchange rates, airflow patterns, and the distribution of fresh air throughout the building. Additionally, the use of air filters, such as HEPA filters, in conjunction with ventilation systems can further improve indoor air quality by capturing and removing finer particles, including allergens and microscopic pollutants.
The Importance of Indoor Ventilation:
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ):
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is a vital aspect of air quality forecast in the indoor environment that directly impacts the health, comfort, and productivity of occupants. IAQ refers to the quality of the air within a building, including the presence of pollutants, odors, allergens, and the overall cleanliness and freshness of the air. Adequate ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal IAQ levels, ensuring that occupants breathe clean and healthy air.
The significance of good IAQ cannot be overstated, as pollution such as poor indoor air quality can have detrimental effects on human health. Several factors contribute to indoor air pollution, including building materials, furniture, cleaning products, cooking activities, and outdoor air pollutants that enter the building. Insufficient ventilation allows these pollutants to accumulate, leading to a range of health problems such as allergies, respiratory issues, fatigue, headaches, and even more severe conditions in some cases.
A primary goal of ventilation systems is to dilute and remove indoor air pollutants, promoting a healthier breathing environment. The exchange of stale, smog, and indoor air with fresh outdoor air helps remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other harmful substances that can be generated or introduced indoors. By introducing a continuous flow of fresh air, ventilation mitigates the concentration of pollutants, reducing the risk of adverse health effects and improving overall well-being.
VOCs, which are emitted from a variety of sources such as paints, adhesives, cleaning products, and furnishings, are a significant concern for indoor air quality. Prolonged exposure to high levels of VOCs can lead to respiratory irritation, headaches, dizziness, asthma, and in some cases, more severe health issues. Proper ventilation aids in the removal of these volatile compounds, ensuring that their concentrations remain within acceptable limits.
Temperature and Humidity Regulation:
Proper temperature and humidity regulation is essential for creating comfortable and healthy indoor environments. Ventilation plays a significant role in maintaining optimal levels of temperature and humidity, ensuring the well-being and comfort of occupants. By facilitating the exchange of air and controlling these factors, ventilation systems contribute to a pleasant and inviting indoor atmosphere.
Temperature Regulation:
Ventilation plays a crucial role in regulating indoor temperatures. Inadequate ventilation can result in stagnant air, leading to higher temperatures and discomfort. During hot weather, the accumulation of heat indoors can be particularly challenging, making the space unpleasant and potentially causing heat-related health issues. Effective ventilation helps dissipate heat by introducing fresh outdoor air and promoting airflow. This process creates a cooling effect and reduces the reliance on mechanical cooling systems, contributing to energy efficiency.
Conversely, in colder weather, ventilation also plays a role in preventing the buildup of excess humidity and condensation, which can contribute to discomfort and potential issues like mold growth. By exchanging moist indoor air with drier outdoor air, ventilation helps maintain appropriate humidity levels, preventing the formation of condensation on windows and surfaces.
Humidity Regulation:
Humidity refers to the amount of moisture present in the air. Proper humidity regulation is crucial for both comfort and health. High humidity levels can make indoor environments feel muggy and uncomfortable. Excessive moisture in the air can also create a conducive environment for mold and mildew growth, which can lead to respiratory issues and damage to building materials. Ventilation systems help control humidity by exchanging moist indoor air with drier outdoor air, reducing the overall moisture content in the space.
On the other hand, low humidity and poor air quality can also cause discomfort, particularly during dry seasons or in arid climates. Dry air can lead to issues such as dry skin, irritated respiratory passages, and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. Ventilation systems can help introduce a controlled amount of moisture to indoor spaces, maintaining optimal humidity levels for comfort and well-being.
By effectively using air pollution levels regulating temperature and humidity through ventilation, indoor environments can achieve a balance that is conducive to human health and comfort. The introduction of fresh air helps create a more pleasant atmosphere, prevents the buildup of heat and excess humidity, and reduces the risk of mold growth and other related issues.
Odor Control:
Odors can significantly impact the indoor environment, making it less inviting and potentially causing discomfort to occupants. Proper ventilation is a key factor in controlling and eliminating unpleasant odors, ensuring a fresh and pleasant indoor atmosphere. By promoting airflow and introducing fresh outdoor air, ventilation systems contribute to effective odor control, enhancing indoor air quality (IAQ), and improving overall comfort.
Sources of Indoor Odors:
Indoor odors can originate from various sources, including cooking activities, pets, cleaning products, chemical off-gassing from building materials and furnishings, and even occupants themselves. These odors can linger and become trapped indoors without adequate ventilation, leading to an unpleasant and stale environment.
The Role of Ventilation in Odor Control:
Ventilation plays a crucial role in eliminating odors from indoor spaces. By facilitating the exchange of air, ventilation systems help remove odorous particles and introduce fresh outdoor air, effectively diluting and replacing stale indoor air. This process is particularly important in enclosed spaces where odors can accumulate and linger.
Cooking odors, for example, can be pervasive and persistent. Without proper ventilation, the smells of food preparation can permeate throughout the entire space, making it less inviting for occupants. Ventilation systems, such as range hoods or exhaust fans in kitchens, effectively remove cooking odors by capturing and expelling them outdoors.
Similarly, chemical odors from cleaning products or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by certain materials can contribute to indoor odors. These odors can have a negative impact on IAQ and even cause health concerns. Ventilation helps remove these odorous particles from the air, reducing their concentration and improving IAQ.
Energy Efficiency:
Well-designed ventilation systems can contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. By incorporating strategies such as natural ventilation, cross-ventilation, or energy recovery ventilation (ERV), buildings can reduce their reliance on mechanical cooling or heating systems. Utilizing natural airflow when possible not only saves energy but also provides a connection to the outdoor environment, enhancing occupants’ well-being and connection to nature.
Building Durability:
Ventilation plays a vital role in preserving the structural integrity and durability of buildings. Moisture accumulation can lead to mold growth, rot, and damage to building materials. By effectively ventilating spaces, excess moisture can be controlled and eliminated, reducing the risk of structural problems and improving the longevity of the building.
Strategies for Effective Indoor Ventilation:
Natural Ventilation:
Opening windows, using vents, and utilizing architectural features to maximize airflow can enhance natural ventilation. This strategy is particularly effective in moderate climates and during seasons with pleasant weather. Natural ventilation not only provides fresh air but also creates a connection between indoor and outdoor environments, promoting a sense of well-being.
Mechanical Ventilation:
Mechanical ventilation systems, such as exhaust fans, supply fans, and balanced ventilation systems, can be installed to ensure consistent and controlled airflow throughout the building. These systems are beneficial in areas where natural ventilation is limited or during extreme weather conditions. Mechanical ventilation allows for precise control of air exchange rates, airflow direction, and filtration, providing a reliable solution for maintaining indoor air quality.
Air Filters:
In conjunction with ventilation systems, using high-quality air filters, such as HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, can effectively remove pollutants, allergens, and airborne particles, further improving indoor air quality. Air filters trap and capture particles as air passes through them, ensuring that the air circulating indoors is clean and free from harmful contaminants.
Regular Maintenance:
Proper maintenance of ventilation systems is crucial to ensure their optimal performance. Regularly cleaning filters, ducts, and vents, as well as inspecting and maintaining mechanical components, will help prevent blockages and ensure efficient airflow. It is important to address any issues promptly to avoid compromised indoor air quality and potential damage to the ventilation system.
The Importance of Professional Expertise in Achieving Optimal Indoor Ventilation
In conclusion, indoor ventilation is a vital component of creating healthy, comfortable, and sustainable indoor environments. Adequate ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining good indoor air quality, regulating temperature and humidity, particle pollution, controlling odors, and promoting energy efficiency. By prioritizing effective ventilation strategies, such as natural and mechanical ventilation, utilizing air filters, and implementing regular maintenance, occupants can enjoy improved health, well-being, and productivity.
Hiring a professional for ventilation-related tasks is highly recommended due to several reasons. First and foremost, professionals have the knowledge and expertise to assess the specific ventilation needs of a building and recommend appropriate strategies. They can evaluate factors such as building size, occupancy, local climate, and regulations to design ventilation systems that are efficient, effective, and compliant.
Professionals also have access to the latest technologies, products, and best practices in the field of many areas of ventilation. They can provide guidance on selecting and installing ventilation equipment, such as fans, air filters, and control systems, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Moreover, professionals have the skills to conduct thorough inspections, maintenance, and troubleshooting of ventilation systems. They can identify and resolve issues that may impact indoor air quality, system efficiency, or occupant comfort. Regular maintenance by professionals ensures current air quality and that ventilation systems continue to operate effectively, preventing potential problems and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Contact the Professionals at EZ Breathe Today! 866-822-7328